Path Operationの設定¶
🌐 Translation by AI and humans
This translation was made by AI guided by humans. 🤝
It could have mistakes of misunderstanding the original meaning, or looking unnatural, etc. 🤖
You can improve this translation by helping us guide the AI LLM better.
path operationデコレータを設定するためのパラメータがいくつかあります。
注意
これらのパラメータはpath operationデコレータに直接渡され、path operation関数に渡されないことに注意してください。
レスポンスステータスコード¶
path operationのレスポンスで使用する(HTTP)status_codeを定義することができます。
404のようにintのコードを直接渡すことができます。
しかし、それぞれの番号コードが何のためのものか覚えていない場合は、statusのショートカット定数を使用することができます:
from fastapi import FastAPI, status
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", status_code=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
🤓 Other versions and variants
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, status
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", status_code=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
そのステータスコードはレスポンスで使用され、OpenAPIスキーマに追加されます。
技術詳細
from starlette import statusを使用することもできます。
FastAPI は開発者の利便性を考慮して、fastapi.statusと同じstarlette.statusを提供しています。しかし、これはStarletteから直接提供されています。
タグ¶
tagsパラメータをstrのlist(通常は1つのstr)と一緒に渡すと、path operationにタグを追加できます:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def read_users():
return [{"username": "johndoe"}]
🤓 Other versions and variants
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def read_users():
return [{"username": "johndoe"}]
これらはOpenAPIスキーマに追加され、自動ドキュメントのインターフェースで使用されます:
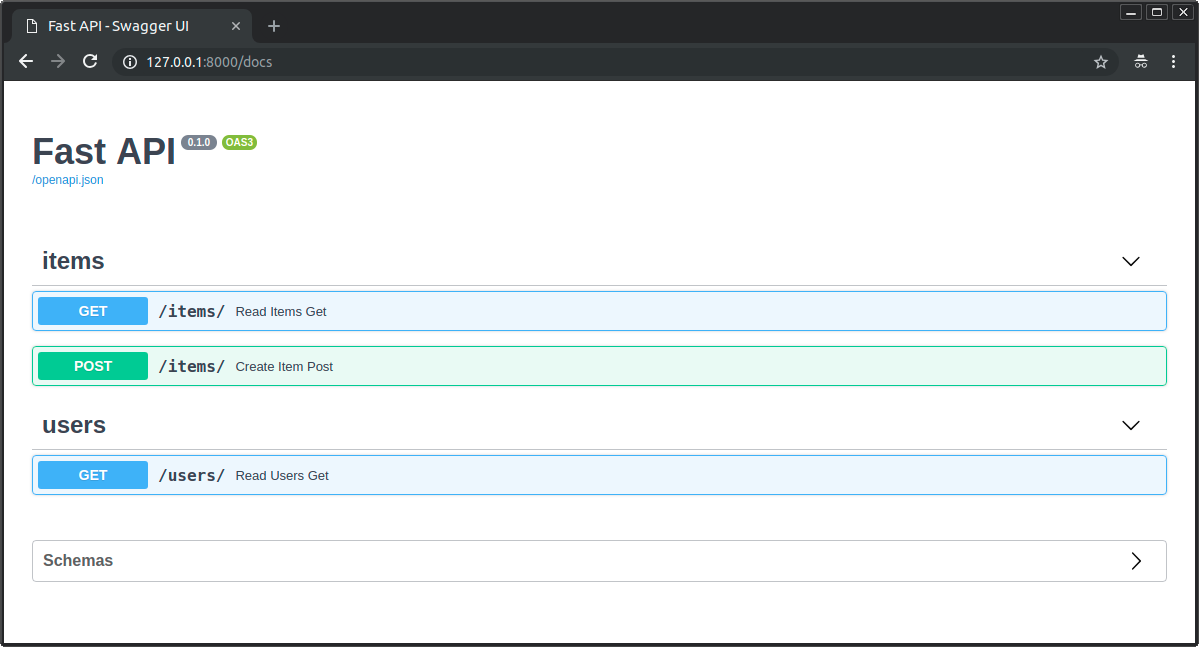
Enumを使ったタグ¶
大きなアプリケーションの場合、複数のタグが蓄積されていき、関連するpath operationsに対して常に同じタグを使っていることを確認したくなるかもしれません。
このような場合、タグをEnumに格納すると理にかなっています。
FastAPI は、プレーンな文字列の場合と同じ方法でそれをサポートしています:
from enum import Enum
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
class Tags(Enum):
items = "items"
users = "users"
@app.get("/items/", tags=[Tags.items])
async def get_items():
return ["Portal gun", "Plumbus"]
@app.get("/users/", tags=[Tags.users])
async def read_users():
return ["Rick", "Morty"]
概要と説明¶
summaryとdescriptionを追加できます:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post(
"/items/",
summary="Create an item",
description="Create an item with all the information, name, description, price, tax and a set of unique tags",
)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
🤓 Other versions and variants
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post(
"/items/",
summary="Create an item",
description="Create an item with all the information, name, description, price, tax and a set of unique tags",
)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
docstringを用いた説明¶
説明文は長くて複数行におよぶ傾向があるので、関数docstring内にpath operationの説明文を宣言できます。すると、FastAPI は説明文を読み込んでくれます。
docstringにMarkdownを記述すれば、正しく解釈されて表示されます。(docstringのインデントを考慮して)
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", summary="Create an item")
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
"""
return item
🤓 Other versions and variants
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", summary="Create an item")
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
"""
return item
これは対話的ドキュメントで使用されます:
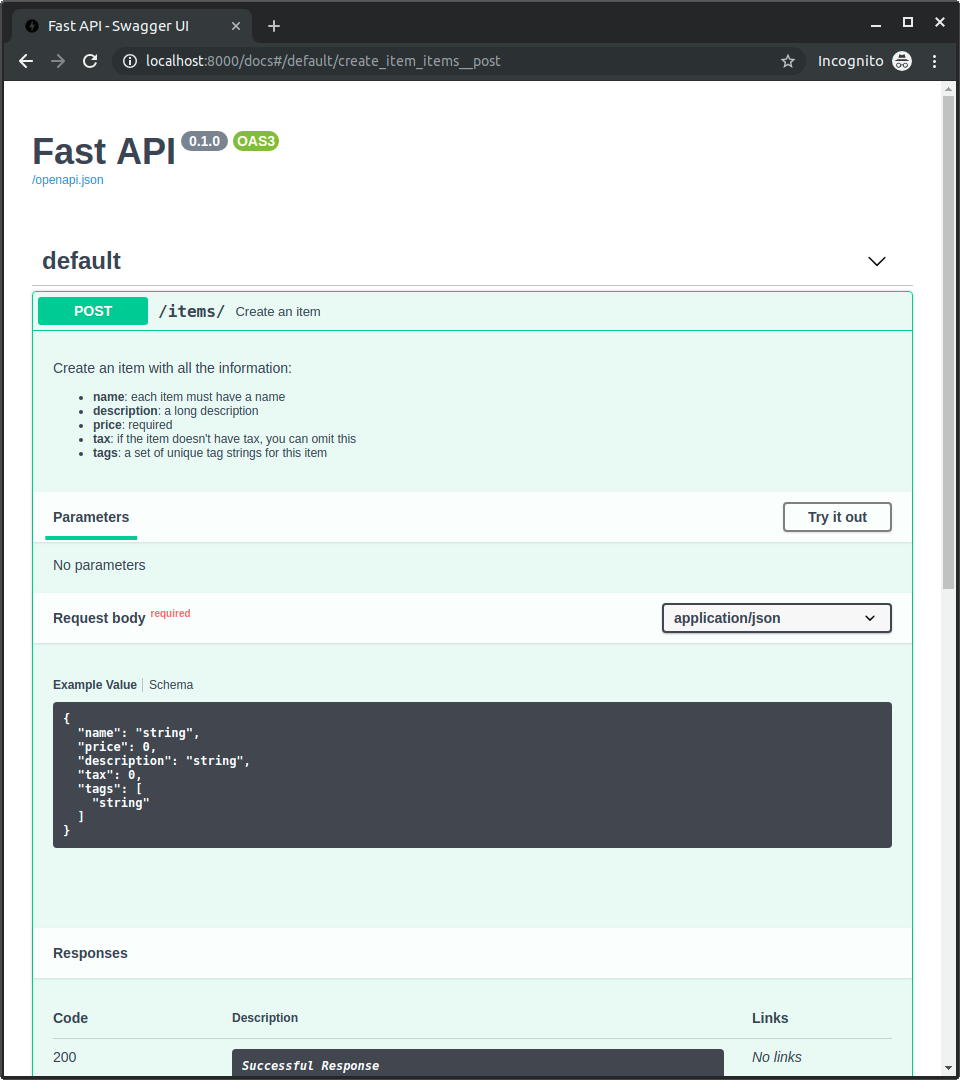
レスポンスの説明¶
response_descriptionパラメータでレスポンスの説明をすることができます。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post(
"/items/",
summary="Create an item",
response_description="The created item",
)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
"""
return item
🤓 Other versions and variants
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post(
"/items/",
summary="Create an item",
response_description="The created item",
)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
"""
return item
情報
response_descriptionは具体的にレスポンスを参照し、descriptionはpath operation全般を参照していることに注意してください。
確認
OpenAPIはpath operationごとにレスポンスの説明を必要としています。
そのため、それを提供しない場合は、FastAPI が自動的に「成功のレスポンス」を生成します。
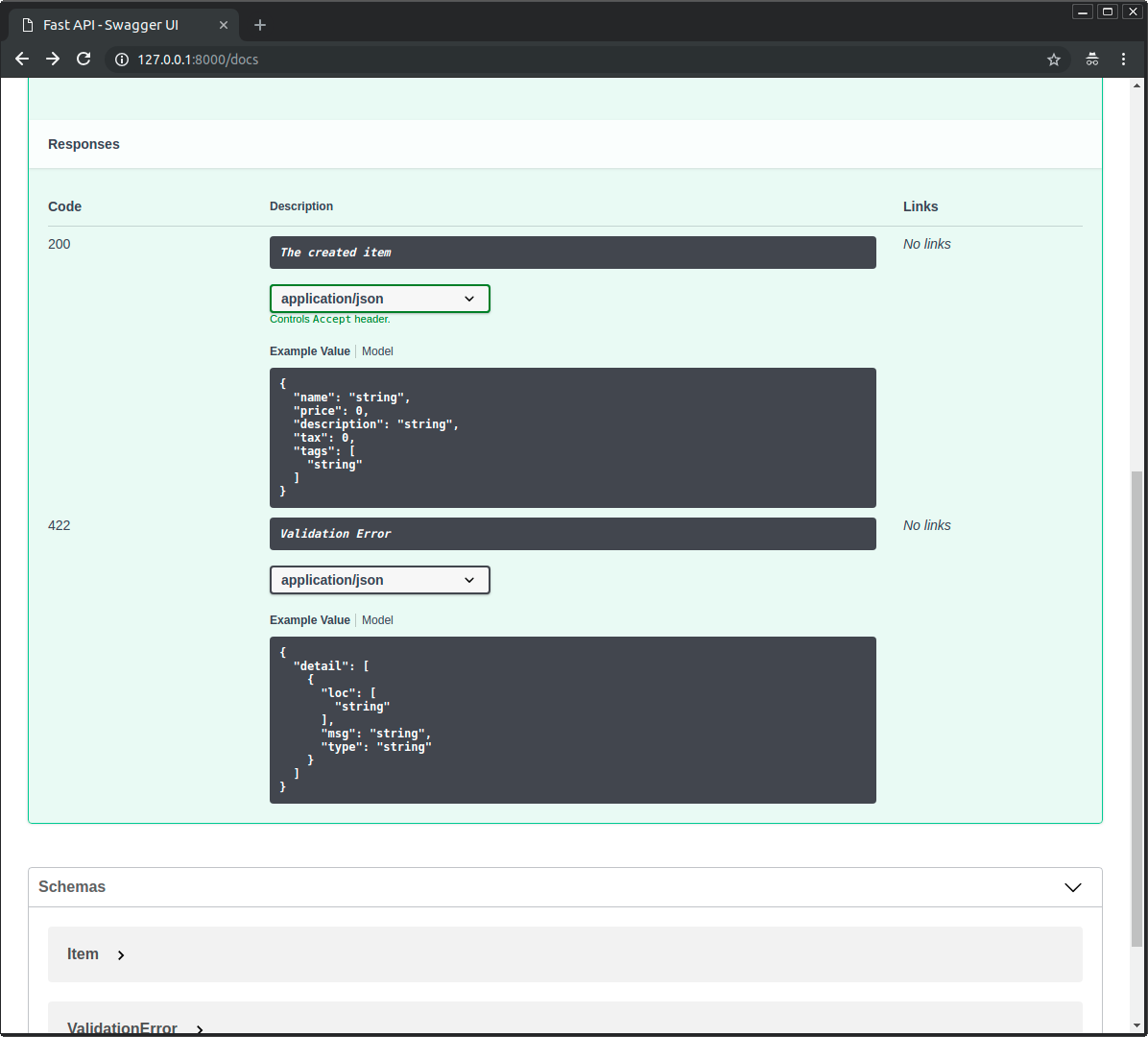
path operationを非推奨にする¶
path operationをdeprecatedとしてマークする必要があるが、それを削除しない場合は、deprecatedパラメータを渡します:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def read_users():
return [{"username": "johndoe"}]
@app.get("/elements/", tags=["items"], deprecated=True)
async def read_elements():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
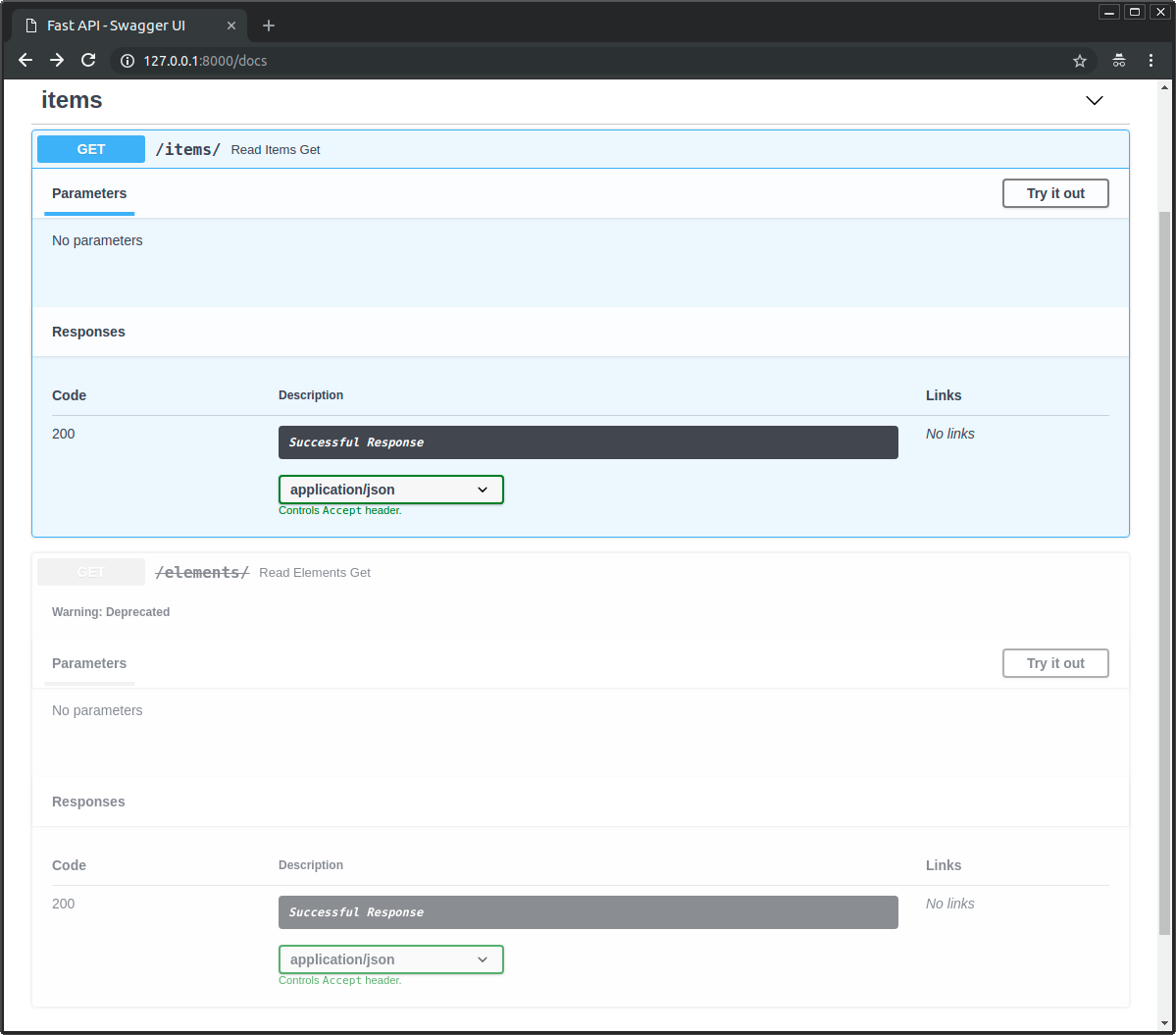
対話的ドキュメントでは非推奨と明記されます:
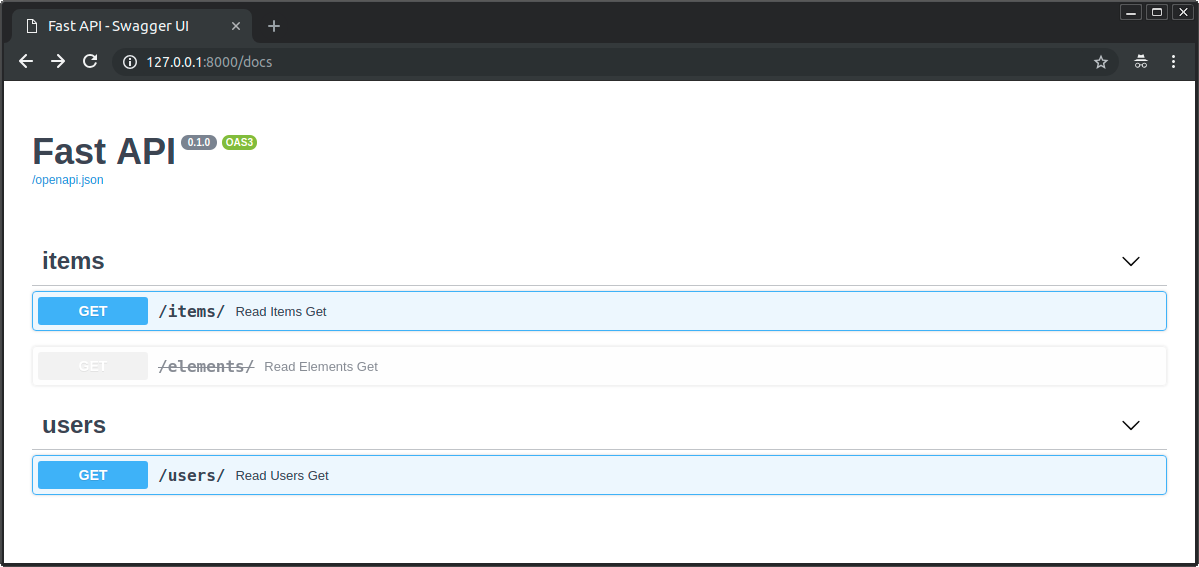
path operationsが非推奨である場合とそうでない場合でどのように見えるかを確認してください:
まとめ¶
path operationデコレータにパラメータを渡すことで、path operationsのメタデータを簡単に設定・追加することができます。