Path Operationの高度な設定¶
🌐 Translation by AI and humans
This translation was made by AI guided by humans. 🤝
It could have mistakes of misunderstanding the original meaning, or looking unnatural, etc. 🤖
You can improve this translation by helping us guide the AI LLM better.
OpenAPI operationId¶
注意
OpenAPIの「エキスパート」でなければ、これはおそらく必要ありません。
path operation で operation_id パラメータを利用することで、OpenAPIの operationId を設定できます。
各オペレーションで一意になるようにする必要があります。
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", operation_id="some_specific_id_you_define")
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
path operation関数 の名前をoperationIdとして使用する¶
APIの関数名を operationId として利用したい場合、すべてのAPI関数をイテレーションし、各 path operation の operation_id を APIRoute.name で上書きすれば可能です。
すべての path operation を追加した後に行うべきです。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.routing import APIRoute
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
def use_route_names_as_operation_ids(app: FastAPI) -> None:
"""
Simplify operation IDs so that generated API clients have simpler function
names.
Should be called only after all routes have been added.
"""
for route in app.routes:
if isinstance(route, APIRoute):
route.operation_id = route.name # in this case, 'read_items'
use_route_names_as_operation_ids(app)
豆知識
app.openapi() を手動で呼び出す場合、その前に operationId を更新するべきです。
注意
この方法をとる場合、各 path operation関数 が一意な名前である必要があります。
異なるモジュール(Pythonファイル)にある場合でも同様です。
OpenAPIから除外する¶
生成されるOpenAPIスキーマ(つまり、自動ドキュメント生成の仕組み)から path operation を除外するには、include_in_schema パラメータを使用して False に設定します。
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", include_in_schema=False)
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
docstringによる説明の高度な設定¶
path operation関数 のdocstringからOpenAPIに使用する行を制限できます。
\f(エスケープされた「書式送り(form feed)」文字)を追加すると、FastAPI はその地点でOpenAPIに使用される出力を切り詰めます。
ドキュメントには表示されませんが、他のツール(Sphinxなど)は残りの部分を利用できます。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", summary="Create an item")
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
\f
:param item: User input.
"""
return item
🤓 Other versions and variants
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", summary="Create an item")
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
\f
:param item: User input.
"""
return item
追加レスポンス¶
path operation に対して response_model と status_code を宣言する方法はすでに見たことがあるでしょう。
それにより、path operation のメインのレスポンスに関するメタデータが定義されます。
追加のレスポンスについても、モデルやステータスコードなどとともに宣言できます。
これについてはドキュメントに章全体があります。 OpenAPIの追加レスポンス で読めます。
OpenAPI Extra¶
アプリケーションで path operation を宣言すると、FastAPI はOpenAPIスキーマに含めるために、その path operation に関連するメタデータを自動的に生成します。
技術詳細
OpenAPI仕様では Operation Object と呼ばれています。
これには path operation に関するすべての情報が含まれ、自動ドキュメントを生成するために使われます。
tags、parameters、requestBody、responses などが含まれます。
この path operation 固有のOpenAPIスキーマは通常 FastAPI により自動生成されますが、拡張することもできます。
openapi_extra パラメータを使って、path operation のOpenAPIスキーマを拡張できます。
OpenAPI Extensions¶
この openapi_extra は、例えば OpenAPI Extensions を宣言するのに役立ちます。
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", openapi_extra={"x-aperture-labs-portal": "blue"})
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "portal-gun"}]
自動APIドキュメントを開くと、その拡張は特定の path operation の下部に表示されます。
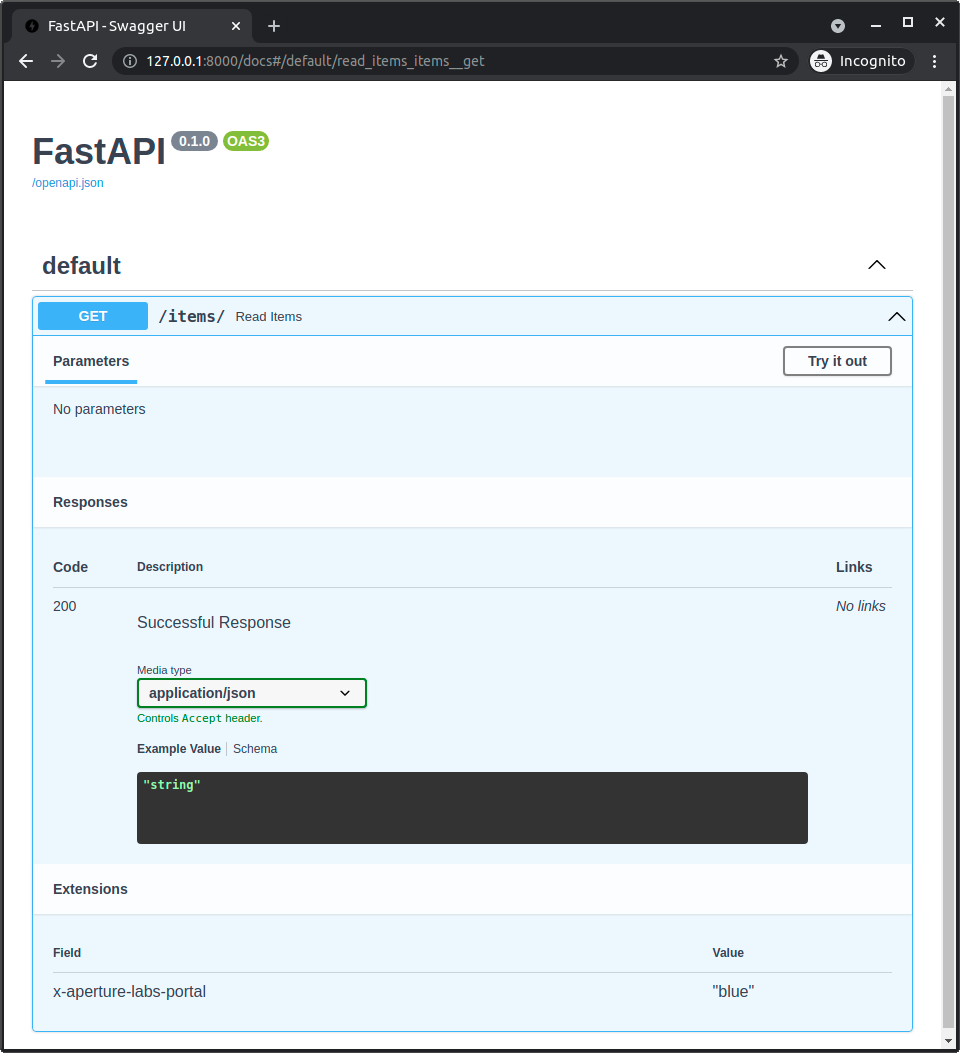
そして(APIの /openapi.json にある)生成されたOpenAPIを見ると、その拡張も特定の path operation の一部として確認できます。
{
"openapi": "3.1.0",
"info": {
"title": "FastAPI",
"version": "0.1.0"
},
"paths": {
"/items/": {
"get": {
"summary": "Read Items",
"operationId": "read_items_items__get",
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Successful Response",
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {}
}
}
}
},
"x-aperture-labs-portal": "blue"
}
}
}
}
カスタムOpenAPI path operation スキーマ¶
openapi_extra 内の辞書は、path operation 用に自動生成されたOpenAPIスキーマと深くマージされます。
そのため、自動生成されたスキーマに追加データを加えることができます。
例えば、Pydanticを使ったFastAPIの自動機能を使わずに独自のコードでリクエストを読み取り・検証することを選べますが、それでもOpenAPIスキーマでリクエストを定義したい場合があります。
それは openapi_extra で行えます。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
app = FastAPI()
def magic_data_reader(raw_body: bytes):
return {
"size": len(raw_body),
"content": {
"name": "Maaaagic",
"price": 42,
"description": "Just kiddin', no magic here. ✨",
},
}
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {
"required": ["name", "price"],
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"price": {"type": "number"},
"description": {"type": "string"},
},
}
}
},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
data = magic_data_reader(raw_body)
return data
この例では、Pydanticモデルを一切宣言していません。実際、リクエストボディはJSONとして parsed されず、直接 bytes として読み取られます。そして magic_data_reader() 関数が、何らかの方法でそれをパースする責務を担います。
それでも、リクエストボディに期待されるスキーマを宣言できます。
カスタムOpenAPI content type¶
同じトリックを使って、PydanticモデルでJSON Schemaを定義し、それを path operation 用のカスタムOpenAPIスキーマセクションに含めることができます。
また、リクエスト内のデータ型がJSONでない場合でもこれを行えます。
例えばこのアプリケーションでは、PydanticモデルからJSON Schemaを抽出するFastAPIの統合機能や、JSONの自動バリデーションを使っていません。実際、リクエストのcontent typeをJSONではなくYAMLとして宣言しています。
import yaml
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
tags: list[str]
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {"application/x-yaml": {"schema": Item.model_json_schema()}},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
try:
data = yaml.safe_load(raw_body)
except yaml.YAMLError:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail="Invalid YAML")
try:
item = Item.model_validate(data)
except ValidationError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail=e.errors(include_url=False))
return item
それでも、デフォルトの統合機能を使っていないにもかかわらず、YAMLで受け取りたいデータのために、Pydanticモデルを使って手動でJSON Schemaを生成しています。
そしてリクエストを直接使い、ボディを bytes として抽出します。これは、FastAPIがリクエストペイロードをJSONとしてパースしようとすらしないことを意味します。
その後、コード内でそのYAMLコンテンツを直接パースし、さらに同じPydanticモデルを使ってYAMLコンテンツを検証しています。
import yaml
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
tags: list[str]
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {"application/x-yaml": {"schema": Item.model_json_schema()}},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
try:
data = yaml.safe_load(raw_body)
except yaml.YAMLError:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail="Invalid YAML")
try:
item = Item.model_validate(data)
except ValidationError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail=e.errors(include_url=False))
return item
豆知識
ここでは同じPydanticモデルを再利用しています。
ただし同様に、別の方法で検証することもできます。